You notice that your patient's submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. You would look for potential infection sites in the
a) hard palate.
b) hard palate and upper lip.
c) hard palate, upper lip and upper central incisor.
d) hard palate, upper lip, upper central incisor and lower first molar.
The skin of the head and neck drains
The scalp drains into the occipital, mastoidand parotid nodes.
Lower eye lid and anterior cheekdrains into buccal LNs.
The cheeksdrain into the parotid, buccaland submandibularnodes.
The upper lipsand sides of the lower lips drain into the submandibular nodes.
Themiddle third of the lower lip drains into the submental nodes
The skin of the neck drains into the cervical nodes.
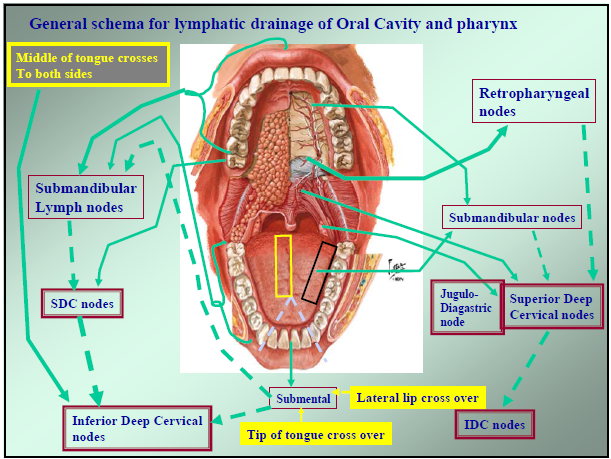
The drainage of the oral structures
Thegingivae drain into the submandibular, submental and upper deep cervical lymph nodes.
The palate lymph vessels may pass to submandibular or superior deep cervical nodes (level II). Retropharyngeal nodes are very rarely involved.
Teeth drain into the submandibular and deep cervical lymph nodes.
Anterior part of mouth floor drain into submental and upper deep cervical.
Posterior part of mouth floor into submandibular and upper deep cervical.